Phasing-out carbon-intensive technologies and business models is a key element for deep decarbonization. Coal is a prime candidate for phase-out and we cannot waste any time. However, every industry decline creates conflicts. Overcoming these conflicts is the key to success.
Renewable energies are often on the top of our heads when we think about the energy transition. We typically look at innovation, new technologies, or new business opportunities. However, industrial decline and technology phase-out are also key elements for our ambition to create low-carbon societies. Decline is the flipside of innovation. Less shiny, conflictive, painful but unavoidable.
Coal phase-out as a key element in the energy transition
As governments around the world devise policies to tackle climate change, coal-fired power generation is often in the focus. Coal not only comes with high CO2 emissions but also contributes to (local) air pollution. Numerous countries including, for example, the UK, Finland, Canada, or Germany have meanwhile formulated policies to phase-out unabated coal-based power generation, and 33 national governments have joined the “Powering Past Coal Alliance”.
A particularly interesting case is the UK. 40 years back, coal contributed to more than 70% of the country’s electricity generation and domestic coal mining was a central source of employment in many regions. Last year, coal was down to around 2% and many expect that the few remaining power plants will be closed before 2025 (which is the official end date of the 2015 government pledge for coal phase-out). So, what happened?
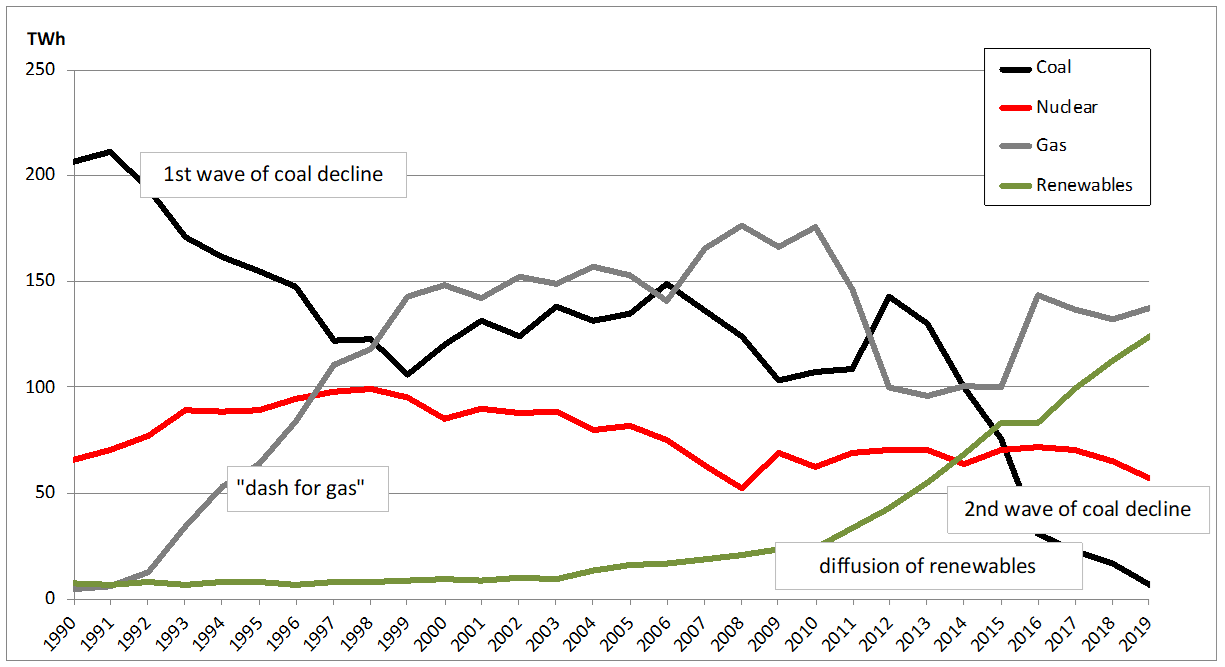
Figure 1: Changes in UK power generation from 1990 to 2019
A scene in two-acts
The UK coal industry declined in two waves (Figure 1). The first happened in the 1990s when electricity markets were liberalized and subsidies for coal mining cut in the wake of Thatcher’s neoliberal policy agenda. The “dash for gas” drove a major part of the country’s coal power plants out of business and the share of coal in the electricity declined to 32% in 2000. The second wave happened just recently. From 2014 to 2019, most of the remaining coal power plants were shut down.
In a recent study, we tracked statements of different groups of actors in the UK by analysing articles on coal and coal phase-out in The Guardian. For many years, the British government and coal industry incumbents tried to defend coal against increasing criticism from environmental NGOs (E-NGOs) and health experts (Figure 2). The main narrative in favor of coal was based on carbon capture and storage technology (CCS) as a potential solution. This hope never materialized, though, and from around 2013 onwards, the resistance by the government and incumbents weakened. The phase-out pledge in 2015 finally sealed the fate of coal.
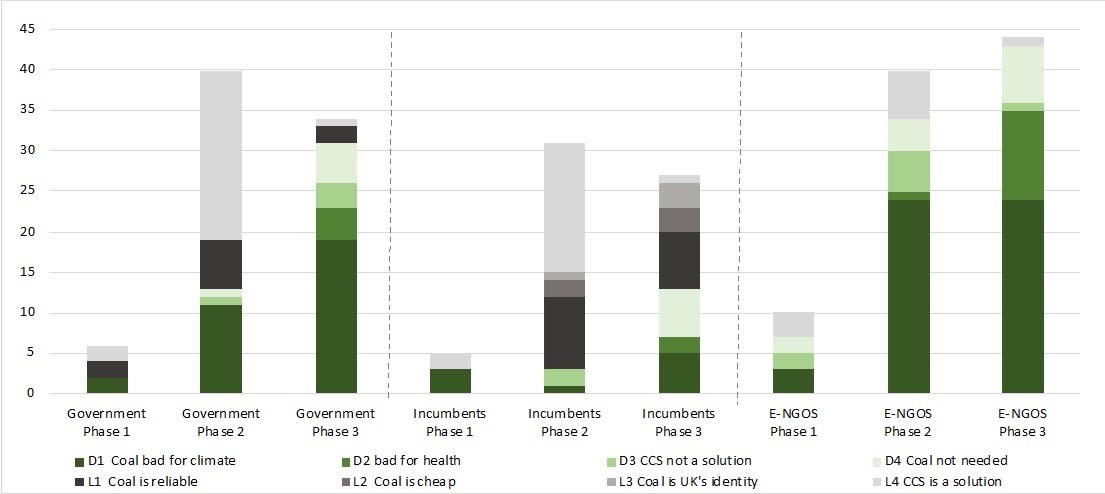
Figure 2: Arguments in favor (grey) and against coal (green) by different actor groups. Phase 1: 2000-07, Phase 2: 2008-12, Phase 3: 2013-17
The public discourse was not the only factor that contributed to coal’s decline in the UK. The 2008 Climate Change Act, the introduction of a carbon price floor in 2013, and various renewable energy policies were important as well. Also, the UK had a pretty old fleet of coal power plants many of which did not comply with EU clean air regulation any more. So, in the end, coal phase-out was less conflictive than anticipated: the jobs in mining were long gone and most power plants were at the end of their lifespan anyway.
Lessons for other phase-outs
The successful coal phase-out in the UK holds several lessons for other countries. First, transitions are contested. So, prepare for resistance, conflicts and conflict resolution. All existing industries have strong ties with political decision-makers and are supported by influential constituencies, most of which perceive the transformation as a threat. In the case of coal, labour unions and social democratic parties often form ‘unholy’ alliances against climate change. Second, and due to this resistance, it is important to develop alternatives, e.g., through innovation and deployment policies. In the UK, these alternatives were renewables and natural gas, which, of course, can only be an interim solution and comes with the risk of another fossil fuel lock-in. It is also important to support new perspectives for those communities and regions who feel left behind. Third, transitions require policies that put pressure on carbon-intensive industries. These may include effective carbon pricing schemes as well as specific phase-out policies. Fourth, transitions often take decades, which is why they require long-term policy guidance. In the UK, this guidance was largely missing and the phase-out pledge by the government only came at a time when the decline was already happening.
Finally, it is important to note that there is no silver bullet for coal phase-out or climate policy more broadly. We often hear that carbon pricing is the key to climate policy. I disagree. Phasing out coal is a policy strategy that can be very effective: it targets a major source of emissions and an industry that cannot escape to unregulated places. Moreover, it focuses on a sector where affordable solutions are available. Of course, coal phase-out is only one policy strategy. Many more will be needed. In fact, to address climate change, we need a broad range of policies that reduce emissions quickly. These policies have to be tailored to the specific context and should be designed with some inherent flexibility so that they can be adapted as the transition progresses.
Cover photo acquired under CC from Flickr
Sources
[1] Isoaho, K., Markard, J., in press. The politics of technology decline: Discursive struggles over coal phase-out in the UK. Review of Policy Research.
[2] Turnheim, B., Geels, F.W., 2012. Regime destabilisation as the flipside of energy transitions: Lessons from the history of the British coal industry (1913-1997). Energy Policy 50, 35-49.
[3] Natural gas, of course, can only be an interim solution and comes with the risk of another fossil fuel lock-in.
[4] Johnstone, P., Hielscher, S., 2017. Phasing out coal, sustaining coal communities? Living with technological decline in sustainability pathways. The Extractive Industries and Society 4, 457-461.
[5] For example, countries differ in terms of geography, energy mix, infrastructure, industry structure, political system and policy culture, societal preferences, level of ambition etc. These differences are best served by combinations of policies (so-called ‘policy mixes’). See: Kern, F., Rogge, K.S., Howlett, M., 2019. Policy mixes for sustainability transitions: New approaches and insights through bridging innovation and policy studies. Research Policy 48, 103832.
[6] Rosenbloom, D., Markard, J., Geels, F.W., Fuenfschilling, L., 2020. Why carbon pricing is not sufficient to mitigate climate change — and how “sustainability transition policy” can help. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117, 8664-8668.
修改评论